Googlebot is a User- Agent . These robots are nicknamed “Web crawlers” or “SEO spiders”, analyze and retrieve resources on web pages. Although it is a simple computer program, knowing how it works is crucial when it comes to natural referencing .
The role of Google SEO Spider
From a directory of URLs already browsed (already crawled) and supplemented by Sitemap data from webmasters (site structure diagram), its role is to:
- Browse and download data from each website by moving from link to link, page to page.
- Determine which site to visit, when and how many pages are linked to it.
- List all new domains to be indexed within search engines, site updates, links to URLs and images, dead links.
- It then uses this data to update the Google index, in addition to adding them to the list of URLs seen previously.
Note that the Google search engine index is the directory of billions of websites made available to users. All new content must be indexed to be visible from the SERP (Search Engine Results Pages). Indexing is therefore the act of making content (domain, website, page, article, etc.) accessible to Internet users from search results. Googlebot only passes through, it in no way legitimizes the content it lists, this is the role of the Google index.
This computer program represents the starting point for the natural referencing of websites, it is the first step in the appearance of content on a search engine. The robot operates simultaneously, and within a few seconds, from computers close to the server site. This way of operating makes it possible not to lose performance or range, but above all not to obstruct the bandwidth of the analyzed servers. That's around a million servers used to crawl the internet, so the IP of a robot is not fixed.
read also: Google Panda becomes Google Coati to fight against thin content
User experience, crawl frequency and budget
The User-Agent puts a point of honor on the user experience
The robot explores a site like a user according to a frequency that it determines itself (according to the popularity of your site, according to your technical choices, etc.). It will always make sure not to compromise the user experience. The robot will then test the site and determine a limit to the “crawl frequency” (ie how many PCs will perform a crawl simultaneously and the waiting time between two iterations) based on:
- The server connection, if the site responds quickly for a significant period of time, its limit will increase. Conversely, if the site takes time to respond or to the slightest server error, its limit will decrease.
- The crawl limit applied by webmasters from Search Console. Note that if it increases, the crawl will not necessarily intensify given that Googlebot configures its actions itself.
A crawl budget to take lightly
The crawl budget is the combination of crawl frequency and the amount of crawl resources. The amount of resources made available for an exploration represents the number of simultaneous connections to a URL and the pause time between two visits.
In many cases, a website is observed the day it goes live. Google says that the crawl budget should be taken lightly.
More resources will be made available for a site:
- Popular, with the aim of keeping it updated within the Google index.
- In migration given the significant number of URLs to index.
- Likely to become obsolete. Google advocates user experience, thus wishing to deindex abandoned sites.
According to Google if your domain has fewer than several thousand URLs then it will be crawled efficiently. Conversely, for sites or pages that have not been involved in any indexing request, Googlebot will restrict its crawling capabilities, even if its limit is not reached.
If in your case it is an important site then you must measure its capacity to be crawled, ie how many times and what resources are made available for crawling. Indeed, depending on the crawl frequency, the Googlebot will occupy a more or less significant portion of your web server's bandwidth, so it is important to know its frequency based on your traffic.
Define Googlebot actions yourself
Google uses many User-Agents like Googlebot to act on the Web. It is possible to tell them what to do, take a look at the list of different User-Agents:
Source: https://support.google.com/webmasters/answer/1061943?hl=fr&ref_topic=4610900
There are then three ways to give them instructions:
Read the Robots.txt file
It is possible to tell a User-Agent to block their passage on your site, but simply blocking Googlebot from the robot.txt file amounts to blocking them all.
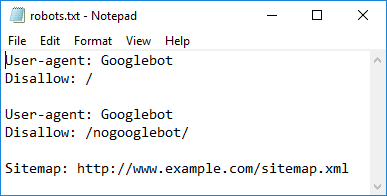
These first two lines give him full access, unlike the next two.
Finally, you tell it the location of the Sitemap data.
We talked about it previously, Googlebot references all the links and then follows them and lists everything that is on the page. That said, you can tell them whether they should follow a link or not.
A note on the robot.txt file is essential! This is the file read first by Google when it crawls a site, this file is present at the very top of the server folder and its location is decisive, if it is not exactly at the top then it does not exist not in Google's eyes.
If the robots.txt file containing the information related to the User-Agent is present in your server, this will increase your SEO credibility. Especially since Google penalizes you if you do not have this file, with the annotation: “robots.txt – file not found”.
Important note: links assigned by “follow” or “nofollow” will be listed and visited without distinction if there is no robot.txt file on the server.
X-Robots-Tag HTTP instructions
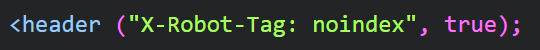
Tell robots not to index this page while still giving it access to the content.

You can combine multiple instructions.
Note: if the attribute: index is specified, the entire content as well as the images will be indexed.
Meta tags
As with the “X-Robots-Tag”, these Meta tags instruct robots to browse and index your page or not.

Guidelines for all User-Agents without distinction.

Do not index the images on the page.
From Search Console, you can refer to the crawl error page, this is where any crawl error encountered by Googlebot is noted. This way you can correct them and move forward.
read also: Google Analytics, the complete guide
Be aware that the slightest error penalizes your natural referencing (SEO) , and therefore your visibility. Although it is impossible to achieve zero errors, Google recommends reading these reports regularly. Furthermore, their support is full of information, advice and even tools on the subject of “crawling”.
Googlebot is therefore the starting point for your natural referencing, so it is wise and productive to take an interest in it for a good SEO strategy. Our SEO agency is made up of experts who analyze the functioning of the Googlebot on a daily basis and who can support you on your SEO projects.

